11. September 2024 By Till Möller
Introduction to the HiveMQ Edge
Integration with the com2m Smart Product Platform for seamless data processing from the edge to the cloud
In today's fast-paced and digitally connected world, the streams of data flowing through our modern infrastructures are almost inexhaustible. From industrial plants to connected vehicles and smart cities - huge amounts of data are being generated and flowing everywhere. But how can this data be processed efficiently and in real time to enable immediate decisions to be made? This is where edge computing comes in.
What is edge computing?
Imagine a factory in which hundreds of machines are in operation around the clock. Each machine is equipped with numerous sensors that continuously collect data on temperature, pressure, vibrations and production status. If all this data were first sent to a central data centre and processed there, there could be considerable delays. These delays can result in critical machine problems not being recognised and rectified in time, which can lead to production downtime and high costs.
With edge computing, on the other hand, the data is processed directly on site, i.e. at the ‘edge’ of the network. This means that the sensors on the machines can analyse this information immediately and take immediate action if necessary - for example, switching off a machine if unusual vibrations are detected that indicate an imminent failure.
A partial solution for edge computing comes from HiveMQ. The HiveMQ Edge software solution provides an MQTT gateway together with various protocol converters. The aim of this solution is to close the gap between OT and IT. This means that HiveMQ Edge is not directly responsible for analysing the data at the network edge, but rather for transferring all data into a standardised namespace. This brings enormous advantages when managing and streaming data via the internal infrastructure.
Key components of the HiveMQ Edge
To achieve the functionality described above, HiveMQ Edge relies on various key components. These include an MQTT broker, an MQTT bridge, various protocol adapters, possible custom adapters and a data hub (see Figure 1).
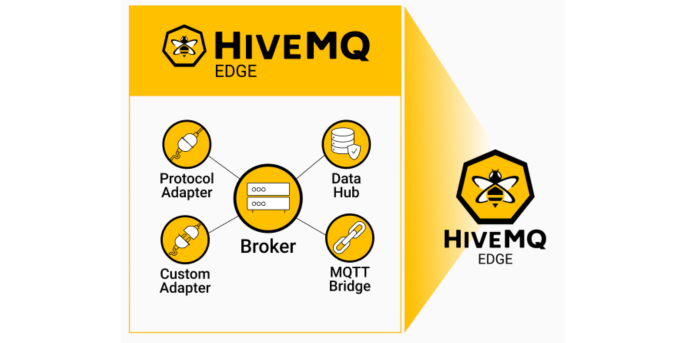
Figure 1: Components of the HiveMQ Edge, source: https://www.hivemq.com/products/hivemq-edge/
The MQTT broker acts on the input side and forwards MQTT 3.1, MQTT 5 and MQTT SN messages directly to the MQTT bridge. Protocol adapters play a central role as they support various communication and automation protocols. These adapters convert the protocols into MQTT messages and thus create a standardised namespace. The currently supported protocols include OPC-UA, Modbus and Siemens S7. If a required protocol is not already integrated, HiveMQ Edge offers the option of creating custom protocol adapters, which then convert their own protocols into MQTT messages and forward them to the MQTT Bridge.
The MQTT Bridge works on the output side of the Edge and acts as a bidirectional connection to Enterprise MQTT Brokers. The Data Hub is available for special requirements for outgoing MQTT messages. This enables the validation and manipulation of messages to ensure optimum data quality. In this way, HiveMQ Edge ensures smooth and efficient communication between different IoT devices and systems in the manufacturing industry.
HiveMQ Edge use with the com2m platform
An ideal use case for HiveMQ Edge is the integration with the com2m Smart Product Platform. Think of the initial example described above, where, for example, the different sensors use different protocols. Since MQTT is one of the main interfaces of the com2m Smart Product Platform, the HiveMQ Edge is perfectly suited to convert the different protocols into MQTT messages and then forward them to the platform (see Fig. 2). Even the simultaneous use of multiple Edge instances poses no problem and ensures seamless and efficient data communication throughout the entire system.

Figure 2: HiveMQ Edge integration, source: see https://www.hivemq.com/products/hivemq-edge/
Advantages and disadvantages of HiveMQ Edge
HiveMQ Edge offers numerous advantages that make it an outstanding solution in combination with the com2m Smart Product Platform. Thanks to powerful plug-and-play integrations, the various protocol adapters can be integrated as required. Custom adapters can also be used if required. Another advantage is the ease of use via the user interface. Offline buffering (store and forward) ensures uninterrupted operation. This means that messages are buffered without data loss in the event of connection interruptions and published later. The creation of a uniform namespace enables seamless data integration into a central data hub, which minimises errors.
However, there are also some disadvantages. The existing protocol adapters may not be able to fulfil all specific requirements. In this case, the effort and expertise required to develop new customised adapters increases. Extended functions such as the Data Hub only offer limited options for analysing and manipulating messages, which may not meet the necessary requirements. There are also technical limitations when creating custom adapters based on MQTT. Despite these disadvantages, HiveMQ Edge is a powerful and flexible solution for modern IoT and edge computing applications.
Conclusion: HiveMQ Edge as a solution to the protocol chaos
To summarise, it can be said that HiveMQ Edge offers an excellent solution for the technical confusion of various protocols. Although HiveMQ Edge cannot be regarded as a classic edge computing application, it still has its raison d'être. As already described, HiveMQ Edge fits perfectly with the com2m Smart Product Platform and creates a standardised data landscape. In complex scenarios, however, the basic functions of HiveMQ Edge are often not sufficient and customised adapters are required.
We will be happy to advise you on how you can use HiveMQ Edge together with the com2m Smart Product Platform in your company and support you with the technical implementation.
Would you like to find out more about our services in the manufacturing industry sector? Then take a look at our website.
Would you like to find out more about exciting topics from the adesso world? Then take a look at our previously published blog posts.

